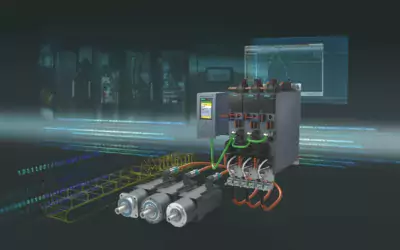
Servo drives are typically embedded controllers or separate control devices that provide feedback signals to motors and other machines.
They are used for tasks such as positioning, speed control, and force control. You might have seen these devices in action if you’ve ever watched a 3D printer, CNC machine or a fanuc robot move its arm around at high speeds. The feedback signal is generated using an encoder or resolver.
Resolvers can be attached directly to the motor shaft or rotated by the motor itself—this is called incremental encoding (IEC). In either case, the position of the shaft is precisely known at all times because it’s being monitored by an encoder/resolver pair on each axis: x-axis, y-axis and z-axis respectively.
Servo drives are embedded controllers or separate control devices that provide feedback signals to motors and other machines.
Servo drives can be used for positioning and speed control, as well as force control in robotics, machine tools and CNC systems.
They are used for tasks such as positioning, speed control, and force control.
Servo drives are used for tasks such as positioning, speed control and force control. They are used in many different applications and industries including:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Packaging machinery
Servo drives can be integrated into machines or used as stand-alone devices that communicate with other equipment via serial communications protocols such as Ethernet or RS232/485/422 (RS-232).
Servo drives are used in many different applications, including robotics, machine tools, and computer numerical control (CNC) systems. They are also known as servo motors or Servo Systems.
A servo motor is a type of electric motor that has been modified to provide closed-loop feedback control over position (and sometimes speed).
This allows the device to maintain a predetermined position without external intervention. The term “servo” comes from their use in radio-controlled models where “servos” were used to remotely control model airplanes and cars by sending radio signals from one device to another via an antennae connected between them through wires laid out on the ground so that there was no interference from other radio signals being broadcasted at the same time near where you live or work because your friend might be listening too instead of working out like he promised me last week when we met up again after school ended for summer break…
The feedback signal is generated using an encoder or resolver.
Servo drives use a feedback signal to regulate the position of the motor. This is done by measuring the actual position of a rotating shaft, and comparing it with what you want that motor to do.
The feedback signal is generated using an encoder or resolver. An encoder generates a pulse every time its magnetic head passes over a magnet embedded in your drive’s gearbox housing (see figure 1). A resolver uses Hall effect sensors to generate electrical signals based on magnetic fields created by passing magnets (see figure 2).
Resolvers can be attached directly to the motor shaft or rotated by the motor itself. A resolver can be attached directly to the motor shaft or rotated by the motor itself. Resolvers are used for position sensing, and they’re a common component in servo drives.
Servo drives are used in many types of automated machines.
Servo drives are used in many different applications. They’re commonly used in robotics, machine tools and computer numerical control (CNC) systems for tasks such as positioning, speed control and force control.
Servo motors are driven by a servo controller that receives commands from a PLC or other controller. A typical servo motor has three wires: power supply voltage; ground; and feedback signal line which carries the position information back to the controller via an encoder wheel or potentiometer sensor attached to it.
Servo drives are used in many different types of automated machines. They’re the industry standard way to control motors and other devices, and they can provide feedback signals that help ensure smooth operation.